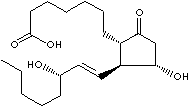
PROSTAGLANDIN E1
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
Cardiovascular, Fibrin Modulator, Fibrinolytic, Hematologic, Platelet aggregation inhibitor, Vasodilator
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Partly soluble
log P
3.2
Health hazard: 2, Flammability: 0, Physical hazards: 0
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions.
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Alprostadil
PubChem Compound Summary - Prostaglandin E1
Drug Bank - Alprostadil
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Prostaglandin E1
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/ - Prostaglandin E1
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Prostaglandin E1
Human Metabolome Database - Prostaglandin E1
http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/
Prostaglandins
are a family of fatty acid derivatives which have a variety of potent
biological activities of a hormonal or regulatory nature. The name
prostaglandin was first given in the 1930’s by the Swedish physiologist
U. S. von Euler to a lipid-soluble acidic substance found in the
seminal plasma, the prostate gland and the seminal vesicles. In
very small amounts this material was found to lower blood pressure
and to stimulate certain smooth muscles to contract. At least 14
prostaglandins occur in human seminal plasma, and many others have
been found in other tissues or prepared synthetically in the laboratory.
Prostaglandin E1 is a vasodilator and inhibitor of platelet aggregation.
It is mainly used to maintain the patency of the ductus arteriosus
in neonates with congenital heart disease until surgery is possible.
Prostaglandin E1 has been used for the treatment of erectile dysfunction5
and was found upon its addition to heparin to enhance “the degree
of anticoagulation as measured by reduced thrombin formation during
cardiopulmonary bypass
Local
Prostaglandin is any member of a group of physiologically active compounds
derived from unsaturated 20-carbon polyunsaturated fatty acids, primarily
arachidonic acid. Prostaglandins are lipids having two long side chains and a 5
carbon ring structure. They are found in normal human semen in highest
concentrations. Their activities affect the nervous system, circulation, female
reproductive organs, and metabolism similar to local hormone functions But they
are not classified in hormones.
Prostaglandin belongs to eicosanoids, biologically active 20-carbon substances including prostaglandins, thromboxanes, prostacyclins, and leukotrienes. Eicosanoids are oxygenated hydrophobic cytokines, small proteins that are the core of communication between immune systems. Prostaglandins, thromboxanes, prostacyclins are derived via the cyclooxygenase pathway, while leukotrienes are via 5-lipoxygenase pathway. Prostaglandins are eicosanoids having a cyclopentane ring. Prostaglandins have two double bonds typically, while leukotrienes have four.
Prostaglandins act in the cells in which they are synthesized and surrounding cells, and their actions and effects vary with concentration, hormonal environment, and cell type. Prostaglandins mediate a wide range of physiological functions, such as control of blood pressure, regulation of muscle, glandular secretion, transmission of nerve impulses, and modulation of inflammation. Specific Prostaglandins designated by adding a letter on PG (the abbreviation for prostaglandin) to indicate the type of ring structure and a numerical subscript to indicate the number of double bonds. The subscript alpha or beta indicates the three-dimensional configuration of alcoholic groups attached to the ring structures. Alpha denotes a substituent below the plane of the ring, beta, above the plane.
|
|
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
99.0 % min
HAZARD OVERVIEW
OSHA Hazards:Target Organ Effect, Toxic by ingestion, Teratogen Target Organs: Smooth muscle., Heart
GHS
PICTOGRAMS


HAZARD STATEMENTS
H301-H361
P STATEMENTS
P281-P301 + P310
![]()
RISK PHRASES
22
SAFETY PHRASES
36